

The bicarbonate serves as an alternate dissolved source of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Prepare 300 ml of bicarbonate solution for each trial. Single hole punch or stout straw Clear plastic cups (4) Timer Light source (lamp) Procedure: 1. You do not need a syringe with a needle!!!! Fresh spinach leaves - from local grocery store. You may have to specifically ask a pharmacist for this. Materials: Sodium bicarbonate (Baking soda) Liquid SoapPlastic syringe (10 cc or larger)-remove needle if there is one! Check local walmart, pharmacy, pet store, baby medicine aisle, etc. The next 3 trials will all occur in different light intensities to test the affect that light has on the rate of photosynthesis based on their production of oxygen.
#SPINACH DISK GRAPH TITLE TRIAL#
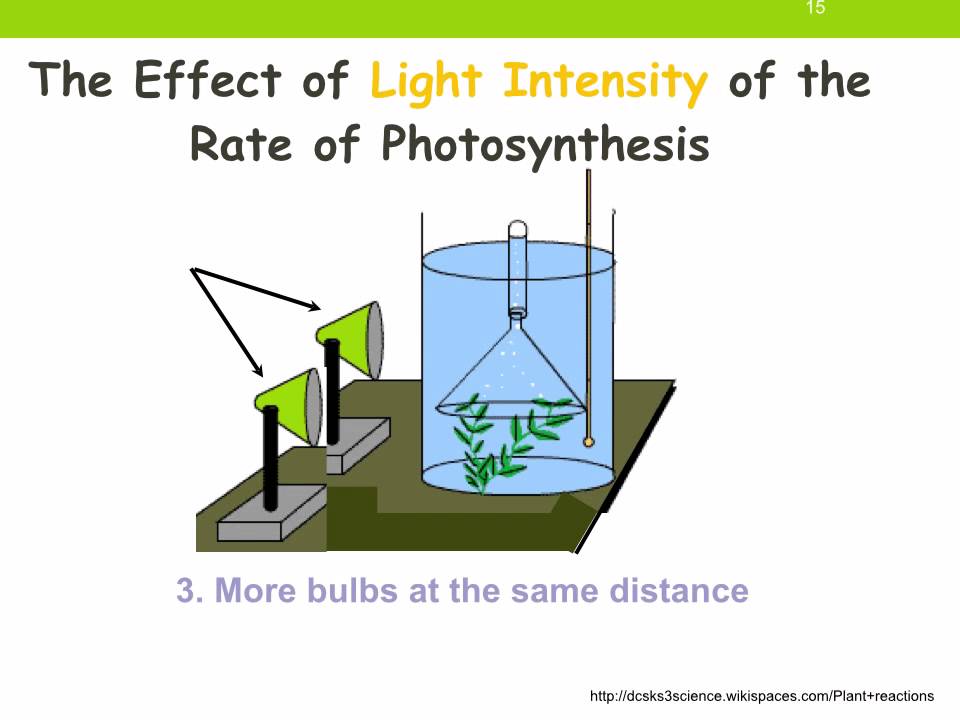
The first trial is the control so you have something to compare your actual experiment to. As the leaves produce oxygen, bubbles forming on the surface of the disks will cause them to rise. Initially, the disks should sink to the bottom of the cup. Dislodge any disks that stick to the side of the container. To control the light received by the leaf disks, a 6 tall cylinder of black paper was used to surround the cup. The leaf disks were then placed in a solution with dissolved CO 2 in a plastic cup with a 2 diameter.

#SPINACH DISK GRAPH TITLE HOW TO#
havent figured out how to graph it because none of the cutout disks of the leaf of a spinach. You will perform 4 trials of this experiment. Pour the spinach leaf discs into the cup of baking soda/detergent solution. Procedure: 12 leaf disks were cut using a hole puncher and had the air extracted using a syringe. Today our group came up with our group name, Team America. As photosynthesis proceeds oxygen is released into the interior of the leaf which changes the buoyancy-causing the disks to rise. Bicarbonate ion serves as the carbon source for photosynthesis. The infiltration solution includes a small amount of Sodium bicarbonate. In this experiment, students will use a syringe to vacuum the air from the spaces in the spongy mesophyll of leaf disks (do not use thick leaves such as. When the air spaces are infiltrated with solution the overall density of the leaf disk increases and the disk sinks. So, the experiment suggests that there is a direct relationship between CO2 concentration and the rate of photosynthesis.In this lab you will be studying the rate that spinach leaf disks rise as an indirect measurement of the net rate of photosynthesis. The results of the experiment supported the hypothesis. The null hypothesis was that the concentration of carbon dioxide will have no effect on the rate of photosynthesis. It was hypothesized that if the concentration of carbon dioxide was increased, then the rate at which photosynthesis occurs will also increase. The ET50 is the time it takes for 50% of the leaf disks to float and is a good indicator of the rate of photosynthesis. Results were calculating by finding the ET50 for each concentration. Unlimited to also enjoy access to over 1 million more titles 3. data entry, saves disk storage space, and allows the.

#SPINACH DISK GRAPH TITLE FREE#
based on The floating leaf disk assay for Investigating photosynthesis. Superfoods Spinach Recipes: Over 60 Quick & Easy Gluten Free Low. Any fresh spinach, consisting mainly of four types: Savoy, Flat or Smooth-Leafed, Semi-Savoy. The cups were then exposed to light for 20 minutes, and the number of disks floating in each cup was measured every minute. Remember to include the parts of the graph: Title and Legend. For each solution of differing carbon dioxide concentration, there were five cups of solution with ten leaf disks per cup, so there was a total of 50 leaf disks per concentration. Any gases within the leaves were then sucked with a syringe, using a specific technique to create a vacuum. There was also a control solution that contained only water. Then solutions of differing concentrations of carbon dioxide, 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8%, and 1.0%, were all prepared, and each solution was spread equally among five cups. Small circular disks were cut out of the spinach leaves using a standard hole puncher.
The purpose of this experiment was to determine the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis in spinach leaves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
